Abstract
BACKGROUND: High dose therapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is commonly used for treating patients with high-risk, relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). Total body irradiation (TBI) has historically been used as a part of the conditioning component based on the exquisite sensitivity of lymphoma to radiation. However, the dose of radiation delivered is limited to major organ toxicity. One strategy to enhance the absorbed dose to target sites and decrease the dose to major organs is to replace external beam TBI with high-dose radioimmunotherapy (RIT). Here we describe the first report of a phase II trial evaluating high-dose I-131-tositumomab (anti-CD20), etoposide (VP-16) and cyclophosphamide (CY) followed by ASCT for high-risk, relapsed or refractory NHL.
METHODS: A single arm, Phase II study was carried out at The Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and University of Washington Medical Center. Patients age < 60 years with histologically confirmed lymphoma expressing the CD20 antigen, with tumor burden < 500 cc, without splenomegaly, acceptable organ function (Cr < 2.0, bilirubin < 1.5mg/dL, normal cardiac ejection fraction, DLCO ≥ 50%), and adequate number of cryopreserved autologous PBSC were eligible. Patients must have had relapsed or refractory disease, except mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) that could be transplanted in first remission. Patients received trace labeled (~10mCi) I-131-tositumomab followed by serial quantitative gamma camera imaging to calculate organ doses and determine the I-131 activity needed to deliver ≤ 25 Gy to critical normal organs. Patients received individualized doses of therapeutic I-131-tositumomab to deliver 25 Gy to the dose limiting normal organ on ~ Day -14, VP-16 60mg/kg on Day -4, CY 100mg/kg on Day -2, followed by ASCT on Day 0. The primary endpoint was progression free survival (PFS) with secondary endpoints of overall survival (OS), engraftment, and non-relapse mortality (NRM).
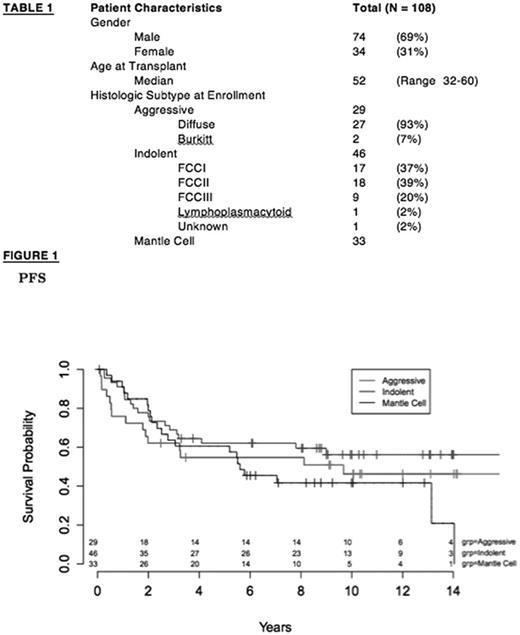
RESULTS: A total of 108 patients were enrolled, treated, and stratified into one of three groups: aggressive lymphoma (n = 29), indolent lymphoma (n = 46), and MCL (n = 33). The median age was 52 years (range 32-60), 69% were male, median prior regimens was 3 (range 1-11), 60% had chemotherapy responsive disease at time of ASCT and 91% had prior Rituximab (R) including 26 of 29 patients with aggressive B-NHL who had received a prior R-chemotherapy based regimen, and 32% had R-refractory disease including 17 of 46 patients with indolent B-NHL. Table 1 shows histologic subtypes at enrollment. Patients received a median of 557 mCi of I-131 (range 231-1353). The most common dose-limiting organs were lung (n = 70), liver (n = 27), and kidneys (n= 6). The median time to engraftment of ANC > 500 and Plt > 20K was 12 and 12 days respectively. The 30-day NRM was 0%, and the 100-day NRM was 2.8%. With a median follow up of 10.1 yrs, the 5 and 10 year PFS for the aggressive, indolent, and MCL groups were 55%, 62%, 61% and 46%, 56%, 42% respectively (figure 1), meeting or exceeding pre-specified phase II benchmarks for this protocol. The 5 and 10 year OS for the aggressive, indolent, and MCL groups were 69%, 80%, 67% and 61%, 70%, 48% respectively. In patients with aggressive B-NHL, prior R-chemotherapy was not associated with inferior PFS (p = 0.7). Likewise, PFS outcomes were similar for R-refractory or R-sensitive indolent B-NHL (p = 0.8). Late myeloid malignancies were seen in 6 (5.6%) patients.
CONCLUSIONS: High-dose I-131-tositumomab (anti-CD20) antibody, VP-16 and CY followed by ASCT appears feasible, safe, and effective in treating B-NHL, resulting in an estimated 42-56% of patients being alive and progression-free at 10 years. Short and long-term toxicity appear comparable to standard conditioning regimens. RIT-containing transplant regimens should thus be evaluated in a prospective randomized trial.
Martin: Procter and Gamble: Equity Ownership; Pfizer: Consultancy; Fresenius, Neovii: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy. Holmberg: Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; JAZZ: Consultancy; Up To Date: Patents & Royalties. Pagel: Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal